
Emeline Pouyet
Associate Scientist at the Center for Scientific Studies in the Arts
An underlying painting, likely by another Barcelona painter, and major compositional changes are among findings
An international partnership of the Northwestern University/Art Institute of Chicago Center for Scientific Studies in the Arts (NU-ACCESS), the Art Gallery of Ontario (AGO) and the National Gallery of Art, Washington, has used multiple modes of light to uncover details hidden beneath the visible surface of Pablo Picasso’s painting “La Miséreuse accroupie” (The Crouching Woman), a major work from the artist’s Blue Period.
The 1902 oil painting, owned by the AGO in Toronto, Canada, depicts a crouching and cloaked woman, painted in white, blues, grays and greens.
With knowledge of an underlying landscape revealed long ago by X-ray radiography at the AGO, researchers used non-invasive portable imaging techniques, including infrared reflectance hyperspectral imaging adapted by the National Gallery of Art and then an X-ray fluorescence imaging instrument developed at Northwestern, to detail buried images connected to other works by Picasso -- including a watercolor recently sold at auction -- as well as the presence of a landscape likely by another Barcelona painter underneath “La Miséreuse accroupie.”
Marc Walton, a research professor of materials science and engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering and co-director of NU-ACCESS, will discuss the collective new findings at a Feb. 17 press briefing at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting in Austin, Texas. He will present a full-scale reproduction of Picasso’s iterative adaptations leading to the final painting. The briefing, “Technology Peers Into Picasso’s Art,” will be held at 9 a.m. CST in Room 6, Level 3, of the Austin Convention Center.
[EDITOR’S NOTE: A separate study of Picasso’s work in three dimensions will be discussed at the same press briefing. Francesca Casadio, the Art Institute of Chicago’s Grainger Executive Director of Conservation and Science and co-director of NU-ACCESS, will talk about the findings from an unprecedented study of five decades of Picasso’s bronzes in the collection of the Musée national Picasso-Paris.]
“Picasso had no qualms about changing things during the painting process,” Walton said. “Our international team -- consisting of scientists, a curator and a conservator -- has begun to tease apart the complexity of ‘La Miséreuse accroupie,’ uncovering subtle changes made by Picasso as he worked toward his final vision.”
NU-ACCESS members who are studying “La Miséreuse accroupie” are Walton, Casadio and postdoctoral fellows Emeline Pouyet and Gianluca Pastorelli.
The researchers used non-invasive methods they adapted to the study of paintings. The state-of-the-art tools enabled the scientists to analyze the painting relatively quickly inside the museum. The key findings of the multidisciplinary international study include:
Picasso painted over another painter’s work after rotating it 90 degrees to the right, using some of the landscape forms in his own final composition of “La Miséreuse accroupie.” Picasso incorporated the lines of the cliff edges into the woman’s back, for example.
Picasso also made a major compositional change, the researchers report. The artist initially painted the woman with a right arm and hand holding a disk but then covered them with her cloak in the final work.
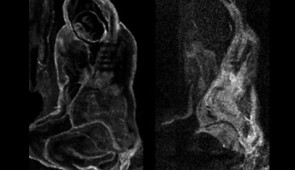
By closely observing “La Miséreuse accroupie,” AGO’s conservation department, now led in this project by senior conservator of paintings Sandra Webster-Cook, had observed distinct textures and contrasting underlying color that peaked through the crack lines and did not match the visible composition. X-ray radiography was the first non-invasive tool used to uncover hidden information in “La Miséreuse accroupie”; it revealed a horizontal landscape by a different Barcelona painter, whose identity remains unknown, under the visible surface of Picasso’s painting.
John Delaney, senior imaging scientist at the National Gallery of Art, then studied the painting with infrared reflectance hyperspectral imaging, which records underlying images depending on their relative transparency of the paint layers. He found an arm and a disk under the surface of the painting. Delaney’s imaging method provides improved visibility of earlier compositional painted elements.
For a more detailed understanding of the repositioned arm, NU-ACCESS scientists next investigated the painting using images generated by their X-ray fluorescence (XRF) scanner. The NU-ACCESS team traveled twice to the AGO in Canada with their portable tools for the study.
This system produces grayscale images showing the distribution of elements associated with various pigments of the painting. The scientists were able to analyze 70 percent of the painting in 24 hours. Together with micro-samples extracted from strategic locations, the XRF results, along with further images generated by Delaney from the hyperspectral reflectance, reveal the steps of creation taken by Picasso.
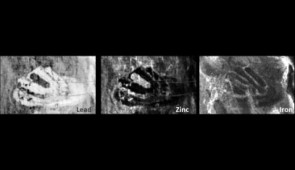
The iron- and chromium-based pigments of the surface layer correlated with the painting’s current structure and its palette of mostly blues (painted with the iron-based Prussian blue and with ultramarine, Picasso’s Blue Period blue of choice) and yellow-greens (painted with chromium-based yellows). The elemental maps of cadmium- and lead-based pigments, however, revealed the presence of the woman’s right arm and hand beneath the visible surface.
The imaging techniques developed by Northwestern and the National Gallery have allowed Kenneth Brummel, the AGO’s assistant curator of modern art, to better understand Picasso’s style, influences and process.
“When we saw the rendering of the lead elemental map, it became clear to me that the arm hidden under the visible surface of ‘La Miséreuse accroupie’ is the same as the proper right arm of a crouching woman in a Picasso watercolor recently sold at auction,” Brummel said. The watercolor is titled “Femme assise” (1902).
Images generated by Delaney -- through the selection of different bandwidths in the near infrared -- confirmed the relationship between “La Miséreuse accroupie” and the watercolor.
“After seeing the lead map from the XRF scanning, we were able to make a map of pigment lead white, which, when overlaid with the false color infrared, gives a more complete image of an upstretched arm, sleeve, disk and fingers,” Delaney said.
“We now are able to develop a chronology within the painting structure to tell a story about the artist’s developing style and possible influences,” said Sandra Webster-Cook, AGO’s senior conservator of paintings.
Further details about the collaboration’s research findings and the implications on Picasso’s developing style and influences will be revealed June 1 at the American Institute of Conservation annual meeting in Houston.
Questions raised by this research on Picasso’s influence and style during his Blue Period will be further explored in a Picasso Blue Period exhibition at the Art Gallery of Ontario and The Phillips Collection in Washington, D.C., in 2020 through 2021.
In a related scientific session the afternoon of Feb. 17 at the AAAS annual meeting, Northwestern’s Aggelos Katsaggelos will explain how he has paired signal processing technology with data collected from the advanced imaging tools used to extract images hidden beneath the surface of “La Miséreuse accroupie.” In addition to presenting the general findings of the investigation by the NU-ACCESS team, Katsaggelos will highlight the use of super-resolution approaches to estimate high-resolution XRF images and how these data are used in the art historical interpretations of the painting.
Katsaggelos, the Joseph Cummings Professor in the McCormick School’s department of electrical engineering and computer science and an NU-ACCESS faculty member, used computational methods to reconstruct the missing pixels of the X-ray fluorescence signal from the acquisition of only approximately 25 percent of the total pixels.
Katsaggelos will speak at the scientific session “Analyzing Picasso: Scientific Innovation, Instrumentation and Education,” to be held from 1:30 to 3 p.m. CST Saturday, Feb. 17, at the AAAS meeting. The symposium, co-organized by Walton, will be held in Room 17B of the Austin Convention Center. In addition to Katsaggelos, the event will include two other speakers discussing different aspects of Picasso’s work. (See details below.)
Ten Northwestern professors will present their work at the AAAS annual meeting. See a full summary at Northwestern Now.
This project with the Art Gallery of Ontario was made possible through NU-ACCESS, which is supported by the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation. The center’s mission is to provide scientific support for the investigation of art collections, to develop new technology to look at art and to research new methods to conserve art for future generations.
Other major NU-ACCESS projects have included studies of the works of Paul Gauguin, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Henri Matisse, Winslow Homer, George Seurat and Mary Cassatt. Most recently, the center spearheaded a study by scientists and Northwestern students of a series of mummy portraits produced in Egypt during the Roman period and a complete intact 1,900-year-old young girl portrait mummy.
Located in Toronto, Canada’s largest city of 6.5 million, the Art Gallery of Ontario (AGO) is one of the largest art museums in North America. The AGO’s collection of close to 95,000 works ranges from cutting-edge contemporary art such as “Untilled” by Pierre Huyghe to European masterpieces such as Peter Paul Rubens’s “The Massacre of The Innocents”; from the vast collection by the Group of Seven to works by established and emerging Indigenous Canadian artists; with a photography collection that tracks the impact of the medium with deep holdings of works by artists such as Garry Winogrand and Diane Arbus; and with focused collections in Gothic boxwood miniatures and Western and Central African art. Drawing on this collection--as well as collaborations with museums around the world--the AGO presents wide-ranging exhibitions and programs, taking special care to showcase diverse and underrepresented artists. A major expansion designed by Frank Gehry in 2008 with lead support from the family of Ken Thomson makes the AGO a highly photographed architectural landmark. Visit ago.ca and follow @AGOToronto to learn more.
The National Gallery of Art, Washington opened to the public on March 17, 1941. Founded by Andrew W. Mellon and accepted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt on behalf of the nation, the gallery serves a singular role in American cultural life. As the nation’s art museum, it is dedicated to preserving, collecting, exhibiting and fostering an understanding of works of art at the highest possible museum and scholarly standards. The gallery’s collection includes more than 150,000 works spanning the history of Western art. Entry to the permanent collection, exhibitions and programs are always free of charge. Visit nga.gov and follow the gallery on Facebook at facebook.com/NationalGalleryofArt and Twitter and Instagram at @ngadc.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/f2a6Ke0rEYk" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>







Associate Scientist at the Center for Scientific Studies in the Arts

Founder and co-Director of the Northwestern University / Art Institute of Chicago Center for Scientific Studies in the Arts