New material removes air-borne droplets
Transparent coating could be painted onto plexiglass barriers, face shields
- Link to: Northwestern Now Story
- Material could stop or slow the spread of infectious diseases by capturing air-borne pathogen-laden droplets
- Clear liquid coating can be applied to any surface, from plastic and glass to wood and textiles
- While air-borne droplets bounce off plastic dividers, they stick to surfaces coated with the new material
- Researcher: ‘Every single droplet effectively removed from indoor air would be a successful elimination of a potential source of transmission’
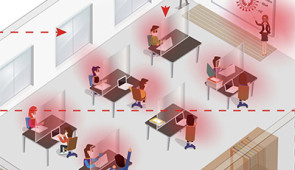
EVANSTON, Ill. — Although plexiglass barriers are seemingly everywhere these days — between grocery store lanes, around restaurant tables and towering above office cubicles — they are an imperfect solution to blocking virus transmission.
Instead of capturing virus-laden respiratory droplets and aerosols, plexiglass dividers merely deflect droplets, causing them to bounce away but remain in the air. To enhance the function of these protective barriers, Northwestern University researchers have developed a new transparent material that can capture droplets and aerosols, effectively removing them from air.
The material is a clear, viscous liquid that can be painted onto any surface, including plastic, glass, wood, metal, stainless steel, concrete and textiles. When droplets collide with the coated surface, they stick to it, get absorbed and dry up. The coating also is compatible with antiviral and antimicrobial materials, so sanitizing agents, such as copper, could be added to the formula.
“Droplets collide with indoor surfaces all the time,” said Northwestern’s Jiaxing Huang, the study’s senior author. “Right now, plexiglass dividers are deviating devices; they deflect droplets. If a surface could actually trap droplets, then every single droplet effectively removed from indoor air would be a successful elimination of a potential source of transmission.”
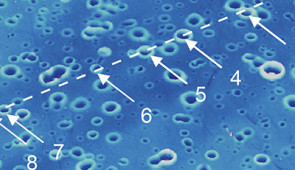
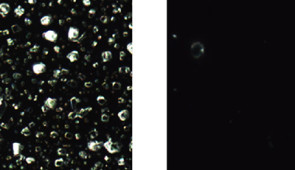
The research was published today (June 16) in the journal Chem. In the study, the researchers found that even when they bombarded surfaces with aerosol droplets — at orders of magnitude higher concentration than typical for an indoor environment — the coated surfaces still captured three times more aerosol droplets than uncoated surfaces.
Huang is a professor of materials science and engineering in Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering. Zhilong Yu, Murak Kadir and Yihan Liu — all members of Huang’s laboratory — co-authored the paper. The team embarked on this project during the stay-at-home order at the beginning of the pandemic.
The main ingredient in the Northwestern team’s material is a polyelectrolyte polymer that is commonly used in a wide variety of cosmetic products. When applied with a blade or brush, the resulting formula yields uniform and conformal coatings on a broad range of indoor surfaces without damaging or discoloring the original material.
Huang’s team found the surfaces also remained transparent and haze-free even when doused with droplets. In other words, the surfaces did not appear filthy or soiled after being showered with droplets. If used on plexiglass barriers, those coated barriers would not need to be cleaned more frequently than uncoated barriers.
Most infectious diseases spread through respiratory droplets and aerosols, which humans release constantly when talking, laughing, singing and exhaling. Because the coating is so versatile, Huang imagines that it could be used on plexiglass barriers and face shields as well as on no-touch or low-touch surfaces, such as walls or even curtains, to eliminate those droplets from the air.
“There are massive areas of indoor surfaces that are barely touched by people or pets. If we repurposed these ‘idling’ surfaces to capture respiratory droplets, then they could become functional ‘devices’ to help reduce air-borne transmission of infectious diseases,” he said. “Surface-trapped pathogens can then be readily inactivated over time, which can be accelerated by pre-applied sanitization ingredients. They also can be removed during routine cleaning.”
While Huang says that face masks are an irreplaceable public health tool to help preventing the spread of infectious droplets, he believes that trapping droplets on surfaces could be another effective tool.
“In a computer game, for example, you don’t want to walk into a battlefield with only one piece of armor,” he said. “It makes sense to leverage multiple layers of defense.”
The study, “Droplet-capturing coatings on environmental surfaces based on cosmetic ingredients,” was supported by a JITRI-Northwestern Research Fellowship awarded from Jiangsu Industrial Technology Research Institute, managed by the Northwestern Initiative for Manufacturing Science and Innovation.
Multimedia Downloads
Material images
Please credit all images to Northwestern University